Abstract
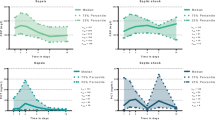
Plasma tocopherol, plasma total lipid levels and tocopherol-lipid ratio were measured every 6 h during 48 h in 12 critically ill patients and compared with those of a control group. The patients were divided into two groups. Group I comprised 6 critically ill patients with ARDS and group II comprised 6 severely ill patients without ARDS. The means for all observations of plasma tocopherol, total lipid levels and tocopherol-lipid ratio in groups I and II were significantly depressed relative to a control group (p<0.0001). The difference in the average tocopherol-lipid ratio between the three groups (p<0.0001) and between the groups I and II was statistically significant (p<0.0001). Our results indicated: (1) a decrease of vitamin E concentrations in the critically ill patients, particularly in ARDS patients; (2) the importance of the relationship between plasma tocopherol and plasma lipids levels in evaluating the deficiency in vitamin E which was evident in ARDS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bieri JG, Corash L, Hubbard S (1983) Medical uses of vitamin E. N Engl J Med 308:1063
Lederer J (1986) Absorption, transport et stockage de la vitamine E et du sélénium. In: Lederer J (ed) Sélénium et Vitamin E. Les deux pompiers de l'organisme. Editions Nauwelaerts, Bruxelles, p 79
McCay PB, King MM (1980) Vitamin E: its role as a biological free radical scavenger and its relationschip to the microsomal mixed function oxidase system. In: Machlin LJ (ed) Vitamin E: a comprehensive treatise. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 289
Lucy JA (1972) Functional and structural aspects of biological membranes: a suggested structural role for vitamin E in the control of membrane permeability and stability. Ann N Y Acad Sci 203:4
Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG (1977) Lipid peroxidation in vivo during vitamin E and selenium deficiency in the rat as monitored by ethane evolution. J Nutr 107:666
Tappel AL, Dillard CJ (1981) In vivo lipid peroxidation: measurement via exhaled pentane and protection by vitamin E. Fed Proc 40:174
Tate RM, Repine JE (1984) Phagocytes, oxygen radicals and lung injury. In: Pryor W (ed) Free radicals in biology, Vol. VI. Academic Press, New York, p 199
Till GO, Hatherill JR, Tourtellotte WW, Lutz MJ, Ward PA (1985) Lipid peroxidation and acute lung injury after thermal trauma to skin. Evidence of a role for hydroxyl radical. Am J Pathol 119:376
Demling RH, Lalonde Ch, Jin L-J, Ryan P, Fox R (1986) Endotoxemia causes increased lung tissue lipid peroxidation in unanesthetized sheep. J Appl Physiol 60:2094
Wong C, Flynn J, Demling RH (1984) Role of oxygen radicals in endotoxin induced lung injury. Arch Surg 119:77
Tate RM, Vanbenthuysen KM, Shasby, McMurtry IF, Repine JE (1982) Oxygen radical-mediated permeability edema and vasoconstriction in isolated perfused rabbit lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis 126:802
Horwitt MK, Harvey CC, Dahm CH, Searcy MT (1972) Relationship between tocopherol and serum lipid levels for determination of nutritional adequacy. Am J Acad Sci 203:223
Bieri JG, Tolliver TJ, Catagnani GL (1979) Simultaneous determination of tocopherol and retinol in plasma and red cells by high pressure liquid chromatography. Am J Clin Nutr 32:2143
Folch J, Les M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) Simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipid animal tissue. J Biol Chem 266:497
Farrell PM, Levine SL, Murphy MD, Adams AJ (1978) Plasma tocopherol levels and tocopherol-lipid relationship in a normal population of children as compared to healthy adults. J Clin Nutr 31:1720
Bieri JG, Farrell PM (1976) Vitamin E. Vitamins Hormones 34:31
Farrell PM, Machlin LJ (1980) Deficiency states, pharmacological effects and nutrient requirements. In: Machlin LJ (ed) Vitamin E: a comprehensive treatise. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 519
Farrell PM, Mischler EH, Gutcher GR (1982) Evaluation of vitamin E deficiency in children with lung disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 393:96
Rubinstein HM, Dietz AA, Srinavasan R (1969) Relation of vitamin E and serum lipids. Clin Chim Acta 23:1
Takeda K, Shimada Y, Amano M, Sakai T, Okada T, Yoshya I (1984) Plasma lipid peroxides and alpha-tocopherol in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 12:957
Richard C, Lemonnier F, Couturier M, Riou B, Auzépy P (1986) Vitamin E and selenium deficiency during acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 133:A203
Richard C, Lemonnier F, Thibaut M, Couturier M, Riou B, Auzépy P (1987) Lipoperoxidation and vitamin E consumption during adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:425
Binder HJ, Herting DC, Hurst V, Finch SC, Spiro HM (1965) Tocopherol deficiency in man. N Engl J Med 273:1289
Horwitt MK, Harvey CC, Duncan GD, Wilson WC (1956) Effects of limited tocopherol intake in man with relationships to erythrocyte hemolysis in lipid oxidation. Am J Clin Nutr 4:408
Lederer J (1986) La carence en vitamine E chez l'homme. In: Lederer J (ed) Sélénium et Vitamine E. Les deux pompiers de l'organisme. Editions Nauwelaerts, Bruxelles, p 230
Alden PB, Svingen BA, Deutschman CS, Johnson SB, Konstantinides FN, Holman RT, Cerra FB (1987) Essential fatty acid status in isolated head injury. J Trauma 27:1039
Birke G, Carlson LA, Liljedahl SO (1965) Lipid metabolism and trauma III. Plasma lipids and lipoproteins in burns. Acta Med Scand 178:337
Carlson LA, Liljedahl SO (1971) Lipid metabolism and trauma IV. Effect of treatment with intravenous fat emulsion on plasma lipids, proteins, and clinical condition of burned patients. Acta Chir Scand 137:123
Carpentier YA, Thonnart N (1987) Parameters for evaluation of lipid metabolism. J Paren Ent Nutr 11:104S
Korthuis RJ, Granger DN (1986) Ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of oxygen-derived free radicals. In: Taylor AE, Matalon S, Ward PA (eds) Physiology of oxygen radicals. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore Maryland, p 217
Tappel AL (1980) Measurement of and protection from in vivo lipid peroxidation. In: Pryor W (ed) Free radical in biology. Academic Press, New York, p 302
Lemoyne M, Van Gossum A, Kurian R, Ostro M, Axler J, Jeejeeboy KN (1987) Breath pentane analysis as an index of lipid peroxidation: a functional test of vitamin E status. Am J Clin Nutr 46:267
Pincemail J, Deby C, Dethier A, Bertrand Y, Lismonde M, Lamy M (1987) Pentane measurement in man as lipoperoxidation index. Bioelectrochem Bioenergetics 18:117
Seeger W, Ziegler A, Wolf HRD (1987) Serum alpha-tocopherol levels after high-dose enteral vitamin E administration in patients with acute respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med 13:395
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertrand, Y., Pincemail, J., Hanique, G. et al. Differences in tocopherol-lipid ratios in ARDS and non-ARDS patients. Intensive Care Med 15, 87–93 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295983
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295983