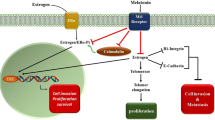
Abstract
Melatonin is involved in many physiological functions and it plays an important role in many pathological processes as well. Melatonin has been shown to reduce the incidence of experimentally induced cancers and can significantly inhibit the growth of some human tumors, namely hormone-dependent cancers. The anticancer effects of melatonin have been observed in breast cancer, both in in vivo with models of chemically induced rat mammary tumors, and in vitro studies on human breast cancer cell lines. Melatonin acts at different physiological levels and its antitumoral properties are supported by a set of complex, different mechanisms of action, involving apoptosis activation, inhibition of proliferation, and cell differentiation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardeland R, Madrid JA, Tal DX et al (2012) Melatonin, the circadian multioscillator system and health: the need for detailed analyses of peripheral melatonin signaling. J Pineal Res 52:139–166
Cardinali DP, Srinivasan V, Brzezinski A et al (2012) Melatonin and its analogues in insomnia and depression. J Pineal Res 52:167–202
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Manchester LC et al (2009) Melatonin and reproduction revisited. Biol Reprod 81:445–456
Rosales-Corral SA, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Coto-Montes A et al (2012) Alzheimer’s disease: pathological mechanisms and the beneficial role of melatonin. J Pineal Res 52:167–202
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Fuentes-Broto L et al (2011) Significance and application of melatonin in the regulation of brown adipose tissue metabolism: relation to human obesity. Obes Rev 12:167–188
Dominguez-Rodriguez A, Abreu-Gonzalez P, Reiter RJ (2012) Melatonin and cardiovascular disease: myth or reality? Rev Esp Cardiol 65:215–218
Korkmaz A, Ma S, Topal T et al (2012) Glucose: a vital toxin and potential utility of melatonin in protecting against the diabetic state. Mol Cell Endocrinol 349(2):128–137
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Mediavilla MD, Tan RJ et al (2010) Scientific basis for the potential use of melatonin in bone diseases: osteoporosis and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Osteoporos ID 830231
Dx Tan, Chen LD, Poeggeler B et al (1993) Melatonin: a potent endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocr J 1:57–60
Hardeland R, Poeggeler B (2008) Melatonin beyond its classical functions. Open Physiol J 1:1–23
Reiter RJ, Paredes SD, Manchester LC et al (2009) Reducing oxidative/nitrosative stress: a newly discovered genre for melatonin. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 44:175–200
Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2011) Melatonin as a natural ally against oxidative stress: a physicochemical examination. J Pineal Res 51:1–16
Sharman EH, Sharman KG, Bondy SC (2011) Extended exposure to dietary melatonin reduces tumor number and size in aged male mice. Exp Gerontol 46:18–22
Cutando A, Aneiros-Fernández J, Aneiros-Cachaza J, Arias-Santiago S (2011) Melatonin and cancer: current knowledge and its application to oral cavity tumours. J Oral Pathol Med 40:593–597
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Mediavilla MD, Alonso-Gonzalez C, Reiter RJ (2012) Melatonin uses in oncology: breast cancer prevention and reduction of the side effects of chemotherapy and radiation. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 21:819–831
Hill SM, Blask DE, Xiang S et al (2011) Melatonin and associated signaling pathways that control normal breast epithelium and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 16:235–245
Lissoni P, Rovelli F (2012) Principles of psychoneuroendocrinoimmunotherapy of cancer. Immunotherapy 4:77–86
Zha L, Fan L, Sun G et al (2012) Melatonin sensitizes human hepatoma cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Pineal Res 52:322–331
Blask DE (2009) Melatonin, sleep disturbance and cancer risk. Sleep Med Rev 13:252–264
Jung-Hynes B, Reiter RJ, Ahmad N (2010) Sirtuins, melatonin and circadian rhythms: building a bridge between aging and cancer. J Pineal Res 48:9–19
Mediavilla MD, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Tan DX (2010) Basic mechanisms involved in the anti-cancer effects of melatonin. Curr Med Chem 17:4462–4481
Greene MW (2012) Circadian rhythms and tumor growth. Cancer Lett 318:115–123
Blask DE, Dauchy RT, Sauer LA (2005) Putting cancer to sleep at night. Endocrine 27(2):179–188
Russel JR, Tan DX, Korkmaz A (2007) Light at night, chronodisruption, melatonin suppression, and cancer risk: a review. Crit Rev Oncog 13:303–328
Georgiou E (1929) Über die Natur und die Pathogenese der Krebstumoren, Radikale Heilung des Krebses bei weißen Mäusen. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol (Zeitschrift für Kregsforshung) 28(1):562–572
Lapin V, Ebels I (1976) Effects of some low molecular weight sheep pineal fractions and melatonin on different tumours in rats and mice. Oncology 33:110–113
Gupta D, Attanasio A, Reiter RJ (1988) The pineal gland and cancer brain research promotion. Tübingen, Germany, pp 1–383
Cohen M, Lippman M, Chabner B (1978) Role of pineal gland in aetiology and treatment of breast cancer. Lancet 2:814–816
Srinivasan V, Spence DW, Pandi-Perumal SR et al (2008) Therapeutic actions of melatonin in cancer: possible mechanisms. Integr Cancer Ther 7:189–203
Villarini A, Pasanisi P, Traina A (2012) Lifestyle and breast cancer recurrences: the DIANA-5 trial. Tumori 98:1–18
Adams SV, Newcomb PA, White E (2012) Dietary cadmium and risk of invasive postmenopausal breast cancer in the VITAL cohort. Cancer Causes Control 23:845–854
DeVita VT Jr, Rosenberg SA (2012) Two hundred years of cancer research. N Engl J Med 366:2207–2214
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Erren TC et al (2009) Light-mediated perturbations of circadian timing and cancer risk: a mechanistic analysis. Integr Cancer Ther 8:354–360
Hansen J, Stevens RG (2011) Night shiftwork and breast cancer risk: overall evidence. Occup Environ Med 68:236–240
Blask DE, Dauchy RT, Brainard GC et al (2009) Circadian stage-dependent inhibition of human breast cancer metabolism and growth by the nocturnal melatonin signal: consequences of its disruption by light at night in rats and women. Integr Cancer Ther 8:347–353
Bartsch C, Bartsch H (2006) The anti-tumor activity of pineal melatonin and cancer enhancing life styles in industrialized societies. Cancer Causes Control 17:559–571
Kerenyi NA, Pandula E, Feuer G (1990) Why the incidence of cancer is increasing: the role of "light pollution". Med Hypotheses 33:75–78
Davis S, Mirick DK, Stevens RG (2001) Night shift work, light at night, and risk of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1557–1562
Hansen J (2001) Increased breast cancer risk among women who work predominantly at night. Epidemiology 12:74–77
Bartsch C, Bartsch H, Jain AK et al (1981) Urinary melatonin levels in human breast cancer patients. J Neural Transm 52:281–294
Bartsch C, Bartsch H, Bellmann O et al (1991) Depression of serum melatonin in patients with primary breast cancer is not due to an increased peripheral metabolism. Cancer 67:1681–1684
Falkson G, Falkson HC, Steyn ME et al (1990) Plasma melatonin in patients with breast cancer. Oncology 47:401–405
Tamarkin L, Cohen M, Roselle D et al (1981) Melatonin inhibition and pinealectomy enhancement of 7–12 dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary tumors in the rat. Cancer Res 41:4432–4436
Blask DE (1984) The pineal: an oncostatic gland? In: Reiter RJ (ed) The pineal gland. Raven Press, New York, pp 253–284
Saez MC, Barriga C, Garcia JJ et al (2005) Melatonin increases the survival time of animals with untreated mammary tumours: neuroendocrine stabilization. Mol Cell Biochem 278:15–20
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Cos S, Fernandez R et al (2003) Melatonin and mammary cancer: a short review. Endocr Relat Cancer 10:153–159
Kubatka P, Bojkova B, Kalicka K et al (2001) Preventive effects of raloxifene and melatonin in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary carcinogenesis in female rats. Neoplasma 48:313–319
Pawlikowski M, Winczyk K, Karasek M (2002) Oncostatic action of melatonin: facts and question marks. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 23:24–29
Cos S, Mediavilla D, Martinez-Campa C et al (2006) Exposure to light-at-night increases the growth of DMBA-induced mammary adenocarcinomas in rats. Cancer Lett 235:266–271
Anisimov VN (2003) The role of pineal gland in breast cancer development. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 46:221–234
Blask DE, Pellettier DB, Hill SM et al (1991) Pineal melatonin inhibition of tumor promotion in the N-nitroso-N-methylurea model of mammary carcinogenesis: potential involvement of antiestrogenic mechanisms in vivo. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 117:526–532
Palmer HJ, Paulson KE (1997) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in signal transduction and gene expression. Nutr Rev 55:353–361
Cerutti PA (1985) Prooxidant states and tumor promotion. Science 227:375–381
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Terron M et al (2007) Melatonin and its metabolites: new findings regarding their production and their radical scavenging actions. Acta Biochim Pol 54:1–9
Burns JK (1973) Administration of melatonin to non-human primates and to women with breast carcinoma. J Physiol 229:38–39
Di Bella L, Scalera G, Rossi MT (1979) Perspectives in pineal function. Prog Brain Res 52:475–478
Lissoni P, Barni S, Meregalli S et al (1995) Modulation of cancer endocrine therapy by melatonin: a phase II study of tamoxifen plus melatonin in metastatic breast cancer patients progressing under tamoxifen alone. Br J Cancer 71:854–856
Lissoni P, Barni S, Cattaneo G et al (1991) Clinical results with the pineal hormone melatonin in advanced cancer resistant to standard antitumor therapies. Oncology 48:448–450
Lissoni P, Barni S, Tancini G et al (1994) A randomised study with subcutaneous low-dose interleukin 2 alone vs interleukin 2 plus the pineal neurohormone melatonin in advanced solid neoplasms other than renal cancer and melanoma. Br J Cancer 69:196–199
Lissoni P, Barni S, Ardizzoia A et al (1994) A randomized study with the pineal hormone melatonin versus supportive care alone in patients with brain metastases due to solid neoplasms. Cancer 73:699–701
Lissoni P, Barni S, Ardizzoia A et al (1992) Randomized study with the pineal hormone melatonin versus supportive care alone in advanced non small cell lung cancer resistant to a first-line chemotherapy containing cisplatin. Oncology 49:336–339
Lissoni P, Barni S, Crispino S et al (1989) Endocrine and immune effects of melatonin therapy in metastatic cancer patients. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 25:789–795
Lissoni P, Barni S, Tancini G et al (1987) Clinical study of melatonin in untreatable advanced cancer patients. Tumori 73:475–480
Panzer A, Viljioen M (1997) The validity of melatonin as an oncostatic agent. J Pineal Res 22:184–207
Mills E, Wu P, Seely D, Guyatt G (2005) Melatonin in the treatment of cancer: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials and meta-analysis. J Pineal Res 39:360–366
Bartsch C, Bartsch H, Karasek M (2002) Melatonin in clinical oncology. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 23(1):30–38
Hill SM, Blask DE (1988) Effects of the pineal hormone melatonin on the proliferation and morphological characteristics of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) in culture. Cancer Res 48:6121–6126
Cos S, Blask DE, Lemus-Wilson A et al (1991) Effects of melatonin on the cell cycle kinetics and oestrogen rescue of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in culture. J Pineal Res 10:36–42
Cos S, Recio J, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ (1996) Modulation of the cell cycle time of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by melatonin. Life Sci 58:811–816
Cucina A, Proietti S, D’Anselmi F et al (2009) Evidence for a biphasic apoptotic pathway induced by melatonin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 46:172–180
L’hermite-Baleriaux M, L’hermite M, Pasteels JM et al (1990) Effect of melatonin on the proliferation of human mammary cancer cell lines. Endocr Soc 140:59
Molis T, Muraoka HG, Castles C et al (1991) Growth regulatory effects of melatonin are linked to the oestrogen response pathway of human breast cancer cells. Endocr Soc 588:177
Shellard SA, Whelan RDH, Hill BT (1989) Growth inhibitory and cytotoxic effects of melatonin and its metabolites on human tumour cell lines in vitro. Br J Cancer 60:288–290
Bizzarri M, Cucina A, Valente MG et al (2003) Melatonin and vitamin D3 increase TGF-beta1 release and induce growth inhibition in breast cancer cell cultures. J Surg Res 110:332–337
Cos S, Fernandez F, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ (1996) Melatonin inhibits DNA synthesis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitro. Life Sci 58:2447–2453
Cos S, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ (2000) Melatonin and mammary pathological growth. Front Neuroendocrinol 21:133–170
Hill SM, Spriggs LL, Simon MA et al (1992) The growth inhibitory action of melatonin on human breast cancer cells is linked to the estrogen response system. Cancer Lett 64:249–256
Dauchy RT, Dauchy EM, Sauer LA et al (2004) Differential inhibition of fatty acid transport in tissue-isolated steroid receptor negative human breast cancer xenografts perfused in situ with isomers of conjugated linoleic acid. Cancer Lett 209:7–15
Blask DE (1993) Melatonin in oncology. In: Yu HS, Reiter RJ (eds) Melatonin. Biosynthesis, physiological effects, and clinical applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 447–475
Brydon L, Roka F, Petit L (1999) Dual signaling of human Me11a melatonin receptors via Gi2, Gi3 and Gq/11 proteins. Mol Endocrinol 13:2025–2038
Dubocovich ML, Markowska M (2005) Functional MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors in mammals. Endocrine 2:101–110
Ram PT, Dai J, Yuan L et al (2002) Involvement of the mt1 melatonin receptor in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 179:141–150
Roka F, Brydon L, Waldhoer M (1999) Tight association of the human Mel (1a)-melatonin receptor and G (i): precoupling and constitutive activity. Mol Pharmacol 56:1014–1024
Dubocovich ML (1988) Luzindole (N-0774): a novel melatonin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:902–910
Dubocovich ML, Masana MI, Iacob S et al (1997) Melatonin receptor antagonists that differentiate between the human Mel1a and Mel1b recombinant subtypes are used to assess the pharmacological profile of the rabbit retina ML1 presynaptic heteroreceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 355:365–375
Collins A, Yuan L, Kiefer TL et al (2003) Overexpression of the MT1 melatonin receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells inhibits mammary tumour formation in nude mice. Cancer Lett 189:49–57
Yuan L, Collins AR, Dai J et al (2002) MT1 melatonin receptor overexpression enhances the growth suppressive effects of melatonin in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 192:147–156
Jawed S, Kim B, Ottenhof T et al (2007) Human melatonin MT1 receptor induction by valproic acid and its effects in combination with melatonin on MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol 560:17–22
Bahia H, Ashman JN, Cawkwell L et al (2002) Karyotypic variation between independently cultured strains of the cell line MCF-7 identified by multicolour fluorescence in situ hybridization. Int J Oncol 20:489–494
Hill SM, Cheng C, Yuan L et al (2011) Declining melatonin levels and MT1 receptor expression in aging rats is associated with enhanced mammary tumor growth and decreased sensitivity to melatonin. Breast Cancer Res Treat 127:91–98
Lai L, Yuan L, Chen Q et al (2008) The Gαi and Gαq proteins mediate the effects of melatonin on steroid/thyroid hormone receptor transcriptional activity and breast cancer cell proliferation. J Pineal Res 45:476–488
Lai L, Yuan L, Cheng Q et al (2009) Alteration of the MT1 melatonin receptor gene and its expression in primary human breast tumors and breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118:293–305
Slominski RM, Reiter RJ, Schlabritz-Loutsevitch N et al (2012) Melatonin membrane receptors in peripheral tissues: distribution and functions. Mol Cell Endocrinol 351:152–166
Pandi-Perumal SR, Trakht I, Srinivasan V et al (2008) Physiological effects of melatonin: role of melatonin receptors and signal transduction pathways. Prog Neurobiol 85:335–353
Guerrero HY, Gauer F, Schuster C et al (2000) Melatonin regulates the mRNA expression of the mt1 melatonin receptor in the rat pars tuberalis. Neuroendocrinology 71:163–169
Gerdin MJ, Masana MI, Ren D et al (2003) Short-term exposure to melatonin differentially affects the functional sensitivity and trafficking of the hMT1 and hMT2 melatonin receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:931–939
Baldwin SW, Travlos GS, Risinger JI et al (1998) Melatonin does not inhibit estradiol-stimulated proliferation in MCF-7 and BG-1 cells. Carcinogenesis 19:1895–1900
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Manchester LC et al (2007) Medical implications of melatonin: receptor-mediated and receptor-independent actions. Adv Med Sci 52:11–28
Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Collin F, Jore D, Gardès-Albert M (2011) Reaction mechanism of melatonin oxidation by reactive oxygen species in vitro. J Pineal Res 50:328–335
Kilic U, Yilmaz B, Ugur M et al (2012) Evidence that membrane-bound G protein-coupled melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2 are not involved in the neuroprotective effects of melatonin in focal cerebral ischemia. J Pineal Res 52:228–235
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Hardeland R et al (2003) Melatonin: a hormone, a tissue factor, an autocoid, a paracoid, and an antioxidant vitamin. J Pineal Res 34:75–78
Hill SM, Blask DE (1986) Melatonin inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation: influence of serum factors prolactin and oestradiol. Abstr Endocr Soc 863:246
Cos S, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ (1995) Melatonin inhibition of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: influence of cell proliferation rate. Cancer Lett 93:207–212
Cos S, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ (1994) Differences between pulsatile or continuous exposure to melatonin on MCF-7 human breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett 85:105–109
Cos S, Blask DE (1990) Effects of melatonin on the anchorage-independent growth of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) in a clonogenic culture system. Cancer Lett 50:115–119
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Mediavilla MD, Alonso-Gonzalez C (2012) Breast cancer therapy based on melatonin. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov 1(6):108–116
Reiter RJ, Fraschini F (1969) Endocrine aspects of the mammalian pineal gland: a review. Neuroendocrinology 5:219–255
Reiter RJ (1980) The pineal and its hormones in the control of reproduction in mammals. Endocr Rev 1:109–131
Barrett P, Bolborea M (2012) Molecular pathways involved in seasonal body weight and reproductive responses governed by melatonin. J Pineal Res 52:376–388
Dubocovich ML, Rivera-Bermudez MA, Gerdin MJ et al (2003) Molecular pharmacology, regulation and function of mammalian melatonin receptors. Front Biosci 8:1093–1108
Cohen M, Lippman M, Chabner B (1978) Role of pineal gland in aetiology and treatment of breast cancer. Lancet 2:814–816
Tamura H, Nakamura Y, Terron MP (2008) Melatonin and pregnancy in the human. Reprod Toxicol 25:291–303
Tamura H, Nakamura Y, Korkmaz A et al (2009) Melatonin and the ovary: physiological and pathophysiological implications. Fertil Steril 92:328–343
Kauppila A, Kivela A, Pakarinen A et al (1987) Inverse seasonal relationship between melatonin and ovarian activity in humans in a region with a strong seasonal contrast in luminosity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65:823–828
Aleandri V, Spina V, Morini A (1996) The pineal gland and reproduction. Hum Reprod Update 2:225–235
Luboshitzky R, Lavie P (1999) Melatonin and sex hormone interrelationships: a review. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 12:355–362
Woo MM, Tai CJ, Kang SK et al (2001) Direct action of melatonin in human granulosa-luteal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4789–4797
Soares JM, Masana MI, Ersahin C et al (2003) Functional melatonin receptors in rat ovaries at various stages of the estrous cycle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:694–702
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Cos S, Mediavilla D et al (2005) Melatonin–estrogen interactions in breast cancer. J Pineal Res 38:217–222
Ram PT, Yuan L, Dai J et al (2000) Differential responsiveness of MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line stocks to the pineal hormone melatonin. J Pineal Res 28:210–218
Del Rio B, Garcia Pedrero JM, Martinez-Campa C et al (2004) Melatonin an endogenous-specific inhibitor of estrogen receptor alpha via calmodulin. J Biol Chem 279:38294–38302
Cos S, Fernandez R, Guezmes A et al (1998) Influence of melatonin on invasive and metastatic properties of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 58:4383–4390
Wilson ST, Blask DE, Lemus-Wilson AM (1992) Melatonin augments the sensitivity of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells to tamoxifen in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75:669–670
Mediavilla MD, Guezmez A, Ramos S et al (1997) Effects of melatonin on mammary gland lesions in transgenic mice overexpressing N-ras proto-oncogene. J Pineal Res 22:86–94
Kiefer TL, Lai L, Yuan L et al (2005) Differential regulation of estrogen receptor alpha, glucocorticoid, receptor and retinoic acid receptor alpha transcriptional activity by melatonin is mediated via different G proteins. J Pineal Res 38:231–239
Garcia-Rato A, Garcia-Pedrero JM, Martinez MA et al (1999) Melatonin blocks the activation of estrogen receptor for DNA binding. FASEB J 13:857–868
Lawson NO, Wee BE, Blask DE et al (1992) Melatonin decreases estrogen receptor expression in the medial preoptic area of inbred (LSH/SsLak) golden hamsters. Biol Reprod 47:1082–1090
Ram PT, Dai J, Yuan L et al (2002) Involvement of the mt1 melatonin receptor in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 179:141–150
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M et al (1995) The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 83:835–839
Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG (2000) The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 14:121–141
Benoit G, Cooney A, Giguere V et al (2006) International Union of Pharmacology LXVI. Orphan nuclear receptors. Pharmacol Rev 58:798–836
Mukherjee R, Davies PJ, Crombie DL et al (1997) Sensitization of diabetic and obese mice to insulin by retinoid X receptor agonists. Nature 386:407–410
Mukherjee R, Jow L, Croston GE et al (1997) Identification, characterization, and tissue distribution of human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) isoforms PPARgamma2 versus PPARgamma1 and activation with retinoid X receptor agonists and antagonists. J Biol Chem 272:8071–8076
Mckenna NJ, O’Malley BW (2002) Minireview: nuclear receptor coactivators—an update. Endocrinology 143:2461–2465
Mckenna NJ, O’Malley BW (2002) Combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear receptors and coregulators. Cell 108:465–474
Becker-Andre M, Wiesemberg I, Schaeren-Wiemers N et al. (1994) Pineal gland hormone melatonin binds and activates an orphan of the nuclear receptor superfamily. J Biol Chem 269:28531–28534
Agez L, LaurentV Pevet P et al (2007) Melatonin affects nuclear orphan receptors mRNA in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei. Neuroscience 144:522–530
Park HT, Baek SY, Kim BS et al (1996) Developmental expression of ‘RZR beta, a putative nuclear-melatonin receptor’ mRNA in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the rat. Neurosci Lett 217:17–20
Baler R, Coon S, Klein DC (1996) Orphan nuclear receptor RZRbeta: cyclic AMP regulates expression in the pineal gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 220:975–978
Naji L, Carillo-Vico A, Guerrero JM et al (2004) Expression of membrane and nuclear melatonin receptors in mouse peripheral organs. Life Sci 74:2227–2236
Bordji K, Grillasca JP, Gouze JN et al (2000) Evidence for the presence of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and gamma and retinoid Z receptor in cartilage. PPARgamma activation modulates the effects of interleukin-1beta on rat chondrocytes. J Biol Chem 275:12243–12250
Smirnov AN (2001) Nuclear melatonin receptors. Biochemistry 66:19–26
Sharma R, Ottenhof T, Rzeczkowska PA et al (2008) Epigenetic targets for melatonin: induction of histone H3 hyperacetylation and gene expression in C17.2 neural stem cells. J Pineal Res 45:277–284
Korkmaz A, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Tan DX et al (2009) Role of melatonin in the epigenetic regulation of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 115:13–27
Korkmaz A (2009) Epigenetic actions of melatonin. J Pineal Res 46:117–118
Korkmaz A, Tamura H, Manchester LC et al (2009) Combination of melatonin and a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist induces apoptosis in a breast cancer cell line. J Pineal Res 46:115–116
Aronika SM, Kraus WL, Katzenellenbogen BS (1994) Oestrogen action via the cAMP signalling pathway: stimulation of adenylate cyclase and cAMP-regulated gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8517–8521
Kiefer T, Ram PT, Yuan L, Hill SM (2002) Melatonin inhibits estrogen receptor transactivation and cAMP levels in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 71:37–45
Ram PT, Kiefer T, Silverman M et al (1998) Estrogen receptor transactivation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by melatonin and growth factors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 141:53–64
Benítez-King G, Ríos A, Martínez A et al (1996) In vitro inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II activity by melatonin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1290:191–196
Pozo D, Reiter RJ, Calvo JR et al (1997) Inhibition of cerebellar nitric oxide synthase and cyclic GMP production by melatonin via complex formation with calmodulin. J Cell Biochem 1(65):430–442
Soto-Vega E, Ramírez-Rodríguez G, Benitez-King G (2004) Melatonin stimulates calmodulin phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J Pineal Res 37:98–106
Garcia-Pedrero JM, Martinez MA, Del Rio B et al (2002) Calmodulin is a selective modulator of estrogen receptors. Mol Endocrinol 16:947–960
Dai J, Inscho EW, Yuan L et al (2002) Modulation of intracellular calcium and calmodulin by melatonin in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 32:112–119
Li Z, Kim SH, Higgins JMG et al (1999) IQGAP1 and calmodulin modulate E-cadherin function. J Biol Chem 274:37885–37892
Blask DE (1997) Systemic, cellular and molecular aspects of melatonin action on experimental breast carcinogenesis. In: Stevens RG, Wilson BW, Anderson LE (eds) The melatonin hypothesis-breast cancer and use of electric power. Battel Press, Columbus, p 189–230
Blask DE, Wilson ST, Zalatan F (1997) Physiological melatonin inhibition of human breast cancer cell growth in vitro: evidence for a glutathione-mediated Pathway. Cancer Res 57:1909–1914
Leung MF, Chov IN (1989) Relationship between l-chloro-2,4-diitrobenzene induced cytoskeletal perturbations and cellular glutathione. Cell Biol Toxicol 5:51–99
Benitez-King G, Anton-Tay F (1993) Calmodulin mediates melatonin cytoskeletal effects. Experientia 49:635–641
Roth JA, Rabin R, Agnello K (1997) Melatonin suppression of PC12 cell growth and death. Brain Res 768:63–70
Yang QH, Xu YN, Xu RK et al (2007) Antiproliferative effects of melatonin on the growth of rat pituitary prolactin-secreting tumor cells in vitro. J Pineal Res 42:172–179
Zhou D, Clarke P, Wang J et al (1996) Identification of a promoter that controls aromatase expression in human breast cancer and adipose stromal cells. J Biol Chem 271:15194–15202
Michael MD, Michael LF, Simpson ER (1997) A CRE-like sequence that binds CREB and contributes to cAMP-dependent regulation of the proximal promoter of the human aromatase P450 (CYP19) gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol 134:147–156
Zhao Y, Aagarwal VR, Mendelson CR et al (1996) Estrogen biosynthesis proximal to a breast tumor is stimulated by PGE2 via cyclic AMP, leading to activation of promoter II of the CYP19 (aromatase) gene. Endocrinology 137:5739–5742
Cardinali DP, Bonanni Rey RA et al (1992) Diurnal changes in cyclic nucleotide response to pineal indoles in murine mammary glands. J Pineal Res 13:111–116
Cos S, Martinez-Campa C, Mediavilla MD et al (2005) Melatonin modulates aromatase activity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 38:136–142
Gonzalez A, Martinez-Campa C, Mediavilla MD et al (2007) Effects of MT1 melatonin receptor overexpression on the aromatase-suppressive effect of melatonin in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 17:947–953
Martinez- Campa C, Gonzalez A, Mediavilla MD et al (2005) Melatonin enhances the inhibitory effect of aminoglutethimide on aromatase activity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 94:249–254
Ryde CM, Nicholls JE, Dowsett M (1992) Steroid and growth factor modulation of aromatase activity in MCF-7 and T47D breast carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 52:1411–1415
Cos S, Blask DE (1994) Melatonin modulates growth factor activity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 17:25–32
Martinez-Campa C, Gonzalez A, Mediavilla MD et al (2009) Melatonin inhibits aromatase promoter expression by regulating cyclooxygenases expression and activity in breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 101:1613–1619
Suzuki T, Miki Y, Nakamura Y et al (2005) Sex steroid-producing enzymes in human breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:701–720
Suzuki T, Miki Y, Nakata T et al (2003) Steroid sulfatase and estrogen sulfotransferase in normal human tissue and breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 86:449–454
Gonzalez A, Cos S, Martinez-Campa C et al (2008) Selective estrogen enzyme modulator actions of melatonin in human breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 45:86–92
Cai Z, Kwintkiewicz J, Young ME et al (2007) Prostaglandin E2 increases cyp19 expression in rat granulosa cells: implication of GATA-4. Mol Cell Endocrinol 263:181–189
Subbaramaiah K, Howe LR, Port ER et al (2006) HER-2/neu status is a determinant of mammary aromatase activity in vivo: evidence for a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res 66:5504–5511
Dong WG, Mei Q, Yu JP et al (2003) Effects of melatonin on the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in rat models of colitis. World J Gastroenterol 9:1307–1311
Mrnka L, Hock M, Rybova M et al (2008) Melatonin inhibits prostaglandin E2 and sodium nitroprusside-induced ion secretion in rat distal colon. Eur J Pharmacol 581:164–170
Deng WG, Tang ST, Tseng HP et al (2006) Melatonin suppresses macrophage cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by inhibiting p52 acetylation and binding. Blood 108:518–5124
Mohan N, Sadeghi K, Reiter RJ et al (1995) The neurohormone melatonin inhibits cytokine, mitogen and ionizing radiation induced NF-kappa B. Biochem Mol Biol Int 37:1063–1070
Chuang JI, Mohan N, Meltz ML et al (1996) Effect of melatonin on NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity in the rat spleen. Cell Biol Int 20:687–692
Esposito E, Iacono A, Muia C et al (2008) Signal transduction pathways involved in protective effects of melatonin in C6 glioma cells. J Pineal Res 44:78–87
Crowe DL, Chandraratna RA (2004) A retinoid X receptor (RXR)-selective retinoid reveals that RXR-alpha is potentially a therapeutic target in breast cancer cell lines, and that it potentiates antiproliferative and apoptotic responses to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands. Breast Cancer Res 6:R546–R555
Fan W, Yanase T, Morinaga H et al (2005) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and retinoid X receptor inhibits aromatase transcription via nuclear factor kappa B. Endocrinology 146:85–92
Molis TM, Spriggs LL, Jupiter Y (1995) Melatonin modulation of estrogen-regulated proteins, growth factors, and proto-oncogenes in human breast cancer. J Pineal Res 18:93–103
Calnaan DPK, Westley BR, May FEB et al (1999) The trefoil peptide TFF1 inhibits the growth of the human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line AGS. J Pathol 188:312–317
Henry JA, Piggott NH, Mallick UK et al (1990) PNR-2/pS2 immunohistochemical staining in breast cancer: correlation with prognostic factors and endocrine response. Br J Cancer 4:615–622
Barnes DM, Gillett CE (1998) Cyclin D1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 52:1–15
Cicatiello L, Addeo R, Sasso A (2004) Oestrogens and progesterone promote persistent CCND1 gene activation during G1 by inducing transcriptional derepression via c-Jun/c-Fos/oestrogen receptor (progesterone receptor) complex assembly to a distal regulatory element and recruitment of cyclin D1 to its own gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol 24:7260–7274
Fu M, Wang C, Li Z, Sakamaky T et al (2004) Minireview: cyclin D1: normal and abnormal functions. Endocrinology 145:5439–5447
Fu M, Rao M, Bouras T et al (2005) Cyclin D1 inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated adipogenesis through histone deacetylase recruitment. J Biol Chem 280:16934–16941
Levine AJ (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Cini G, Neri B, Pacini A et al (2005) Antiproliferative activity of melatonin by transcriptional inhibition of cyclin D1 expression: a molecular basis for melatonin-induced oncostatic effects. J Pineal Res 39:12–20
Abbas T, Dutta A (2009) p21 in cancer: intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer 9:400–414
Mediavilla MD, Cos S, Sanchez-Barcelo EJ (1999) Melatonin increases p53 and p21WAF1 expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitro. Life Sci 65:415–420
Rimler A, Matzkin H, Zisapel N (1999) Cross talk between melatonin and TGF-1 in human benign prostate epithelial cells. Prostate 40:211
Molis TM, Priggs LL, Hill SM (1994) Modulation of estrogen receptor mRNA expression by melatonin in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 8:1683–1690
Czeczuga-Semeniuk E, Anchim T, Dziecioł J et al (2004) Can transforming growth factor-β1 and retinoids modify the activity of estradiol and antiestrogens in MCF-7 breast cancer cells? Acta Biochim Pol 51:733–745
Blask DE, Sauer LA, Dauchy RT (2002) Melatonin as a chronobiotic/anticanceragent: cellular, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of action and their implications for circadian-based cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem 2:113–132
Leon-Blanco MM, Guerrero JM, Reiter JR et al (2003) Melatonin inhibits telomerase activity in the MCF-7 tumour cell line both in vitro and in vivo. J Pineal Res 35:204–211
Martinez-Campa CM, Alonso-Gonzalez C, Mediavilla MD et al (2008) Melatonin down-regulates hTERT expression induced by either natural estrogens (17b-estradiol) or metalloestrogens (cadmium) in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 268:272–277
Leon-Blanco MM, Guerrero JM, Reiter RJ et al (2004) RNA expression of human telomerase subunits TR and TERT is differentially affected by melatonin receptor agonists in the MCF-7 tumor cell line. Cancer Lett 216:73–80
Blasco MA (2007) The epigenetic regulation of mammalian telomeres. Nat Rev Genet 8:299–309
Reiter RJ (2004) Mechanisms of cancer inhibition by melatonin. J Pineal Res 37:213–214
Sainz RM, Mayo JC, Rodriguez C et al (2003) Melatonin and cell death: differential actions on apoptosis in normal and cancer cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:1407–1426
Sánchez-Hidalgo M, Guerrero JM, Villegas I (2012) Melatonin, a natural programmed cell death inducer in cancer. Curr Med Chem (in press)
Karasek M, Winczyk K, Kunert-Radk J et al (1998) Antiproliferative effects of melatonin and CGP52608 on the murine colon 38 adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Neuroendocrinol Lett 19:71–78
Winczyk K, Pawlikowski M, Lawnicka H et al (2002) Effects of melatonin and melatonin receptors ligand N-[(4-methoxy-1H-indol-2yl) methyl] propanamide on murine Colon 38 cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Neuroendocrinol Lett 1:50–54
Motilva V, García-Mauriño S, Talero E et al (2011) New paradigms in chronic intestinal inflammation and colon cancer: role of melatonin. J Pineal Res 51:44–60
Carbajo-Pescador S, García-Palomo A, Martín-Renedo J et al (2011) Melatonin modulation of intracellular signaling pathways in hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cell line: role of the MT1 receptor. J Pineal Res 51:463–471
Garcia-Santos G, Antolin I, Herrera F et al (2006) Melatonin induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cancer cells. J Pineal Res 41:130–135
El-Missiry MA, Abd EL-Aziz AF (2000) Influence of melatonin on proliferation and antioxidant system in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 151:119–125
Rubio S, Estevez F, Cabrera J et al (2007) Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis by melatonin in human myeloid HL-60 cells. J Pineal Res 42:131–138
Trubiani O, Recchioni R, Moroni F et al (2005) Melatonin provokes cell death in human B-lymphoma cells by mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathway activation. J Pineal Res 39:425–431
Leja-Szpak A, Jaworek J, Pierzchalski P et al (2010) Melatonin induces pro-apoptotic signaling pathway in human pancreatic carcinoma cells (PANC-1). J Pineal Res 49:248–255
Gonzalez A, del Castillo-Vaquero A, Miro-Moran A et al (2011) Melatonin reduces pancreatic tumor cell viability by altering mitochondrial physiology. J Pineal Res 50:250–260
Um HJ, Park JW, Kwon TK (2011) Melatonin sensitizes Caki renal cancer cells to kahweol-induced apoptosis through CHOP-mediated up-regulation of PUMA. J Pineal Res 50:359–366
Wolfler A, Caluba HC, Abuja PM et al (2001) Prooxidant activity of melatonin promotes fas-induced cell death in human leukemic Jurkat cells. FEBS Lett 502:127–131
Bejarano I, Espino J, Barriga C et al (2011) Pro-oxidant effect of melatonin in tumour leucocytes: relation with its cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic effects. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 108:14–20
Casado-Zapico S, Martín V, García-Santos G et al (2011) Regulation of the expression of death receptors and their ligands by melatonin in haematological cancer cell lines and in leukaemia cells from patients. J Pineal Res 50:345–355
Cos S, Mediavilla MD, Fernandez R et al (2002) Does melatonin induce apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitro? J Pineal Res 32:90–96
Czeczuga-Semeniuk E, Wołczyński S, Anchim T et al (2002) Effect of melatonin and all-trans retinoic acid on the proliferation and induction of the apoptotic pathway in the culture of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Pol J Pathol 53:59–65
Eck-Enriquez KM, Yuan L, Duffy L et al (1998) A sequential treatment regimen with melatonin and all-trans retinoic acid induces apoptosis in MCF-7 tumour cells. Br J Cancer 77:2129–2137
Eck-Enriquez KM, Kiefer TL, Spriggs LL et al (2000) Pathways through which a regimen of melatonin and retinoic acid induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 61:229–239
Abd El-Aziz MA, Hassan HA, Mohamed MH et al (2005) The biochemical and morphological alterations following administration of melatonin, retinoic acid and Nigella sativa in mammary carcinoma: an animal model. Int J Exp Pathol 86:383–396
Momand J, Wu HH, Dasgupta G (2000) MDM2–master regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Gene 242:15–29
RozieresS DE, Maya R, Oren M et al (2000) The loss of MDM2 induces p53-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 19:1691–1697
Inoue T, Geyer RK, Yu ZK et al (2001) Downregulation of MDM2 stabilizes p53 by inhibiting p53 ubiquitination in response to specific alkylating agents. FEBS Lett 490:196–201
Proietti S, Cucina A, D’Anselmi F et al (2011) Melatonin and vitamin D3 synergistically down-regulate Akt and MDM2 leading to TGFβ-1-dependent growth inhibition of breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 50:150–158
Lopez-Burillo S, Tan DX, Mayo JC et al (2003) Melatonin, xanthurenic acid, resveratrol, EGCG, vitamin C and a-lipoic acid differentially reduce oxidative DNA damage induced by Fenton reagents: a study of their individual and synergistic actions. J Pineal Res 34:269–277
Mao L, Yuan L, Hill SM. Inhibition of cell proliferation and blockade of cell invasion by melatonin in human breast cancer cells mediated through multiple signaling pathways. Paper presented at: 97th annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research 2006 Washington, DC. Abstract 495
Cos S, Fernandez R (2000) Melatonin effects on intercellular junctional communication in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 29:166–171
Trosko JE, Chang CC, Madhukar BV et al (1990) Chemical, oncogene and growth factor inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication: an integrative hypothesis of carcinogenesis. Pathobiology 58:265–278
Hamada J, Takeichi N, Kobayashi H (1987) Inverse correlation between the metastatic capacity of cell clones derived from a rat mammary carcinoma and their intercellular communication with normal fibroblasts. Gann 78:1175–1178
Crespo D, Fernandez-Viadero C, Verdura R et al (1994) Interaction between melatonin and estradiol on morphological and morphometric features of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 16:215–222
Swarnakar R, Paul S, Singh LP et al (2011) Matrix metalloproteinases in health and disease: regulation by melatonin. J Pineal Res 50:8–20
Sainz RM, Mayo JC, Tan DX et al (2005) Melatonin reduces prostate cancer cell growth leading to neuroendocrine differentiation via a receptor and PKA independent mechanism. Prostate 63:29–43
Rodriguez-Garcia A, Mayo JC, Heria D et al (2012) Phenotypic changes caused by melatonin increased sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to cytokine-induced apoptosis. J Pineal Res (in press)
Roberts K (1974) Cytoplasmic microtubules and their functions. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 28:371–420
Ingber DE (2003) Tensegrity, II. How structural networks influence cellular information processing networks. J Cell Sci 116:1397–1408
Wang N, Tytell JD, Ingber DE (2009) Mechanotransduction at a distance: mechanically coupling the extracellular matrix with the nucleus. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:75–82
Pourati J, Maniotis A, Speigel DM et al (1998) Is cytoskeletal tension a major determinant of cell deformability in adherent endothelial cells? Am J Physiol 274:C1283–C1289
Hammond TG, Lewis FC, Goodwin TJ et al (1999) Gene expression in space. Nat Med 5:359
Stein GS, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL et al (1999) Implications for interrelationships between nuclear architecture and control of gene expression under microgravity conditions. FASEB 13:S157–S166
Chen CS, Mrksich M, Huang S et al (1997) Geometric control of cell life and death. Science 276:1425–1428
Huang S, Ingber DE (2000) Shape-dependent control of cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis: switching between attractors in cell regulatory networks. Exp Cell Res 261:91–103
D’Anselmi F, Valerio MC, Cucina A et al (2011) Metabolism and cell shape in cancer: a fractal analysis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:1052–1058
Raz A, Geiger B (1982) Altered organization of cell-substrate contacts and membrane-associated cytoskeleton in tumor cell variants exhibiting different metastatic capabilities. Cancer Res 42:5183–5190
Benitez-King G, Tunez I, Bellon A et al (2003) Melatonin prevents cytoskeletal alterations and oxidative stress induced by okadaic acid in N1E−115 cells. Exp Neurol 182:151–159
Wang LH (2004) Molecular signaling regulating anchorage independent growth of cancer cells. Mt Sinai J Med 71:361–367
Bharadwaj S, Thanawala R, Bon G et al (2005) Resensitization of breast cancer cells to anoikis by tropomyosin-1: role of Rho kinase-dependent cytoskeleton and adhesion. Oncogene 24:8291–8303
Raftopoulou M, Hall A (2004) Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev Biol 265:23–32
Huerto-Delgadillo L, Anton-Tay F, Benitez-King G (1994) Effects of melatonin on microtubule assembly depend on hormone concentration: role of melatonin as a calmodulin antagonist. J Pineal Res 17:55–62
Benitez-King G, Soto-Vega E, Ramirez-Rodriguez G (2009) Melatonin modulates microfilament phenotypes in cancer cells: implications for adhesion and inhibition of cancer cell migration. Histol Histopathol 24:789–799
Ortiz-Lopez L, Morales-Mulia S, Ramiraz-Rodriguez G et al (2009) ROCK-regulated cytoskeletal dynamics participate in the inhibitory effect of melatonin on cancer cell migration. J Pineal Res 46:15–21
Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Meza I, Hernandez ME et al (2003) Melatonin induced cyclic modulation of vectorial water transport in kidney-derived MDCK cells. Kidney Int 63:1356–1364
Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Ortiz-Lopez L, Benitez-King G (2007) Melatonin increases stress fibers and focal adhesions in MDCK cells: participation of Rho-associated kinase and protein kinase C. J Pineal Res 42:180–190
Yuan J, Shi GX, Shao Y et al (2008) Calmodulin bound to stress fibers but not microtubules involves regulation of cell morphology and motility. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:284–293
Benitez-King G (2006) Melatonin as a cytoskeletal modulator: implications for cell physiology and disease. J Pineal Res 40:1–9
Lee SE, Kim SJ, Youn JP et al (2011) MicroRNA and gene expression analysis of melatonin-exposed human breast cancer cell lines indicating involvement of the anticancer effect. J Pineal Res 51:345–352
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Mediavilla MD, Alonso-Gonzalez C et al (2012) Melatonin uses in oncology: breast cancer prevention and reduction of the side effects of chemotherapy and radiation. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 21:819–831
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proietti, S., Cucina, A., Reiter, R.J. et al. Molecular mechanisms of melatonin’s inhibitory actions on breast cancers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 2139–2157 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1161-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1161-8