Abstract
Purpose
Cervical cancer is the second most prevalent cancer in women worldwide. Survival of patients has been improved by cisplatin-based chemotherapy, but its effectiveness is limited due to its adverse effects on many tissues, especially nephrotoxicity. To optimize the efficacy of CDDP, we propose a combination therapy using natural products with minimal side effects. Vitamin C being a natural antioxidant is capable of selectively targeting cancer cells at pharmacological concentrations. Vitamin C synergistically enhances the activity of chemotherapeutic agents without increasing toxicity to normal cells. Therefore, we exploited co-therapy with cisplatin and vitamin C to kill cervical cancer cells.
Methods
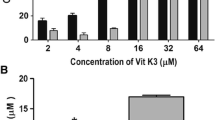
We elucidated the role of CDDP and VC on cervical cancer cell line (SiHa) by using cell growth assays, DNA fragmentation analysis, comet assay, in vitro morphological assessment of apoptosis (AO/EB and DAPI staining), ROS analysis by DCFDA, flow cytometry, biochemical assays (GST, GSH, NO, catalase, TPA) and Western blotting.
Results
Our results clearly demonstrated that CDDP and VC treatment exhibited ameliorative effect on induction of cell death by p53 overexpression and generation of hydrogen peroxide in SiHa cells, thereby reducing the dosage of CDDP required to induce cell death in cancer cells.
Conclusions
These studies provide novel approaches to combat cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDDP:
-
Cisplatin
- VC:
-
Vitamin C
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- TPA:
-
Total peroxidase assay
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- AO:
-
Acridine orange
- EB:
-
Ethidium bromide
References
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Ahamad MS, Siddiqui S, Jafri A et al (2014) Induction of apoptosis and antiproliferative activity of naringenin in human epidermoid carcinoma cell through ROS generation and cell cycle arrest. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0110003
An SH, Kang JH, Kim DH, Lee MS (2011) Vitamin C increases the apoptosis via up-regulation p53 during cisplatin treatment in human colon cancer cells. BMB Rep 44:211–216. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2011.44.3.211
Attardi DL, Jacks T (1999) The role of p53 in tumour suppression: lessons from mouse models. Cell Mol Life Sci C 55:48–63. doi:10.1007/s000180050269
Bao J, Haldane C, Lee Y et al (2013) Effectiveness of intravenous Vitamin C in combination with conventional chemotherapy in cancer treatment : a review. J IHP-Contin Educ 1:72–80
Blancher C, Jones A (2001) SDS -PAGE and Western Blotting techniques. In: Brooks SA, Schumacher U (eds) Metastasis research protocols: volume I: analysis of cells and tissues, vol I. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 145–162
Cadenas E, Davies KJA (2000) Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic Biol Med 29:222–230. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00317-8
Cepeda V, Fuertes MA, Castilla J, Alonso C, Quevedo CPJ (2007) Biochemical mechanisms of cisplatin cytotoxicity. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 7:3–18
Céraline J, Deplanque G, Duclos B et al (1998) Inactivation of p53 in normal human cells increases G2/M arrest and sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. Int J Cancer 75:432–438. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19980130)75:3<432:AID-IJC17>3.0.CO;2-A
Chen Q, Espey MG, Krishna MC et al (2005) Pharmacologic ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer cells: action as a pro-drug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13604–13609. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506390102
Chiang CD, Song EJ, Yang VC, Chao CC (1994) Ascorbic acid increases drug accumulation and reverses vincristine resistance of human non-small-cell lung-cancer cells. Biochem J 301:759–764
Collins AR, Dusinská M, Gedik CM, Stĕtina R (1996) Oxidative damage to DNA: do we have a reliable biomarker? Environ Health Perspect 104:465–469. doi:10.1289/ehp.96104s3465
Cuzick J, Arbyn M, Sankaranarayanan R et al (2008) Overview of human papillomavirus-based and other novel options for cervical cancer screening in developed and developing countries. Vaccine 26:K29–K41. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.06.019
Danesi CC, Bellagamba BC, Dihl RR et al (2010) Evaluation of the genotoxicity of cisplatin, paclitaxel and 5-fluorouracil combined treatment in the Drosophila wing-spot test. Food Chem Toxicol 48:3120–3124. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.08.005
Du J, Cullen JJ, Buettner GR (2012) Ascorbic acid: chemistry, biology and the treatment of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1826:443–457. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.06.003
Garaj-Vrhovac V, Kopjar N (2003) The alkaline Comet assay as biomarker in assessment of DNA damage in medical personnel occupationally exposed to ionizing radiation. Dans les dernières années, l’électrophorèse sur gel de cellule unique (SCGE) ou test des comètes a été largement utilisé po. Mutagenesis 18:265–271
Griess P (1879) Bemerkungen zu der abhandlung der H.H. Weselsky und Benedikt Ueber einige azoverbindungen. Chem Ber 12:426–428
Habig WH, Pabst MJJW (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139. doi:10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2010.23.013
Hahm E, Jin D-H, Kang JS et al (2007) The molecular mechanisms of Vitamin C on cell cycle regulation in B16F10 murine melanoma. J Cell Biochem 102:1002–1010. doi:10.1002/jcb.21336
Head KA (1998) Ascorbic acid in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Altern Med Rev 3:174–186
Henson DE, Block G, Levine M (1991) Ascorbic acid: biologic functions and relation to cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 83:547–550. doi:10.1093/jnci/83.8.547
Hernandez-Flores G, Ortiz-Lazareno PC, Lerma-Diaz JM et al (2011) Pentoxifylline sensitizes human cervical tumor cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by suppressing NF-kappa B and decreased cell senescence. BMC Cancer 11:483. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-483
Hooker DJ, Mobarok M, Anderson JL et al (2012) A new way of measuring apoptosis by absolute quantitation of inter-nucleosomally fragmented genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gks334
Jurado R, Lopez-Flores A, Alvarez A, García-López P (2009) Cisplatin cytotoxicity is increased by mifepristone in cervical carcinoma: an in vitro and in vivo study. Oncol Rep 22:1237–1245
Kartalou M, Essigmann JM (2001) Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen 478:23–43. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(01)00141-5
Kim J, Lee S-D, Chang B et al (2012a) Enhanced antitumor activity of Vitamin C via p53 in cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med 53:1607–1615. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.079
Kim J, Lee S-D, Chang B et al (2012b) Enhanced antitumor activity of Vitamin C via p53 in cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med 53:1607–1615. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.079
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A et al (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 534:15–20. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00251-6
Kurbacher CM, Wagner U, Kolster B et al (1996) Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) improves the antineoplastic activity of doxorubicin, cisplatin, and paclitaxel in human breast carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Lett 103:183–189. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(96)04212-7
Kwon S-B, Kim M-J, Yang JM et al (2016) Cudrania tricuspidata Stem Extract Induces Apoptosis via the Extrinsic Pathway in SiHa Cervical Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 11:e0150235. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150235
Liu K, Liu P-C, Liu R, Wu X (2015) Dual AO/EB staining to setect apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells compared with flow cytometry. Med Sci Monit Basic Res 21:15–20. doi:10.12659/MSMBR.893327
Mikirova Na, Ichim TE, Riordan NH (2008) Anti-angiogenic effect of high doses of ascorbic acid. J Transl Med 6:50. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-6-50
Moron MS, Kepierre JW, Mannervick B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 582:67–78. doi:10.1016/0304-4165(79)90289-7
Ohno S, Ohno Y, Suzuki N et al (2009) High-dose Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) therapy in the treatment of patients with advanced cancer. Anticancer Res 29:809–815
Pajaniradje S, Mohankumar K, Pamidimukkala R et al (2014) Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of sesbania grandiflora leaves in human cancer cells. Biomed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2014/474953
Park S, Han S-S, Park CH et al (2004) L-Ascorbic acid induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells via hydrogen peroxide-mediated mechanisms. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2180–2195. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2004.04.005
Pias EKAT, AW TY (2002) Apoptosis in mitotic competent undifferentiated cells is induced by cellular redox imbalance independent of reactive oxygen species production. FASEB J 16:781–790. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0784com
Rahman T, Hosen I, Islam MMT, Shekhar HU (2012) Oxidative stress and human health. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 03:997–1019. doi:10.4236/abb.2012.327123
Ratnam DV, Ankola DD, Bhardwaj V et al (2006) Role of antioxidants in prophylaxis and therapy: a pharmaceutical perspective. J Control Release 113:189–207. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.04.015
Reddy VG, Khanna N, Singh N (2001) Vitamin C augments chemotherapeutic response of cervical carcinoma HeLa cells by stabilizing P53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 282:409–415. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4593
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Udensi UK, Tchounwou PB (2014) Dual effect of oxidative stress on leukemia cancer induction and treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 33:106. doi:10.1186/s13046-014-0106-5
van Bladeren PJ (2000) Glutathione conjugation as a bioactivation reaction. Chem Biol Interact 129:61–76. doi:10.1016/S0009-2797(00)00214-3
Verma AK, Sachin K, Saxena A, Bohodar HB (2005) Release kinetics from bio polymeric nanoparticles encapsulating protein synthesis inhibitor-cycloheximide, for possible therapeutic applications. Curr Pharm Biotech 6:121–130
Verrax J, Buc Calderon P (2008) The controversial place of Vitamin C in cancer treatment. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1644–1652
Verrax J, Vanbever S, Stockis J et al (2007) Role of glycolysis inhibition and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation in necrotic-like cell death caused by ascorbate/menadione-induced oxidative stress in K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemic cells. Int J Cancer 120:1192–1197. doi:10.1002/ijc.22439
Waalkes MP, Liu J, Kasprzak KS, Diwan BA (2006) Hypersusceptibility to cisplatin carcinogenicity in metallothionein-I/II double knockout mice: production of hepatocellular carcinoma at clinically relevant doses. Int J Cancer 119:28–32. doi:10.1002/ijc.21245
Weijl N, Elsendoorn T, Lentjes EGW et al (2004) Supplementation with antioxidant micronutrients and chemotherapy-induced toxicity in cancer patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Cancer 40:1713–1723. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2004.02.029
Wlodkowic D, Skommer J, Darzynkiewicz Z (2009) Flow cytometry-based apoptosis detection. Methods Mol Biol 559:1–14. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-017-5
Wolff SP (1994) Ferrous ion oxidation in presence of ferric ion indicator xylenol orange for measurement of hydroperoxides [J]. Methods Enzymol 233:182–189
Yun J, Mullarky E, Lu C et al (2015) Vitamin C selectively kills KRAS and BRAF mutant colorectal cancer cells by targeting GAPDH. Science 350:1391–1396. doi:10.1126/science.aaa5004
Zhang JH, Xu M (2000) DNA fragmentation in apoptosis. Cell Res 10:205–211. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290049
Zilfou JT, Lowe SW (2009) Tumor suppressive functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:1–12. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a001883
Zitka O, Skalickova S, Gumulec J et al (2012) Redox status expressed as GSH:GSSG ratio as a marker for oxidative stress in paediatric tumour patients. Oncol Lett 4:1247–1253. doi:10.3892/ol.2012.931
Acknowledgments
Ankita Leekha is thankful to Jamia Millia Islamia for providing her Non-Net fellowship.
Funding
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript, and this is purely academic research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leekha, A., Gurjar, B.S., Tyagi, A. et al. Vitamin C in synergism with cisplatin induces cell death in cervical cancer cells through altered redox cycling and p53 upregulation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 2503–2514 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2235-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2235-z